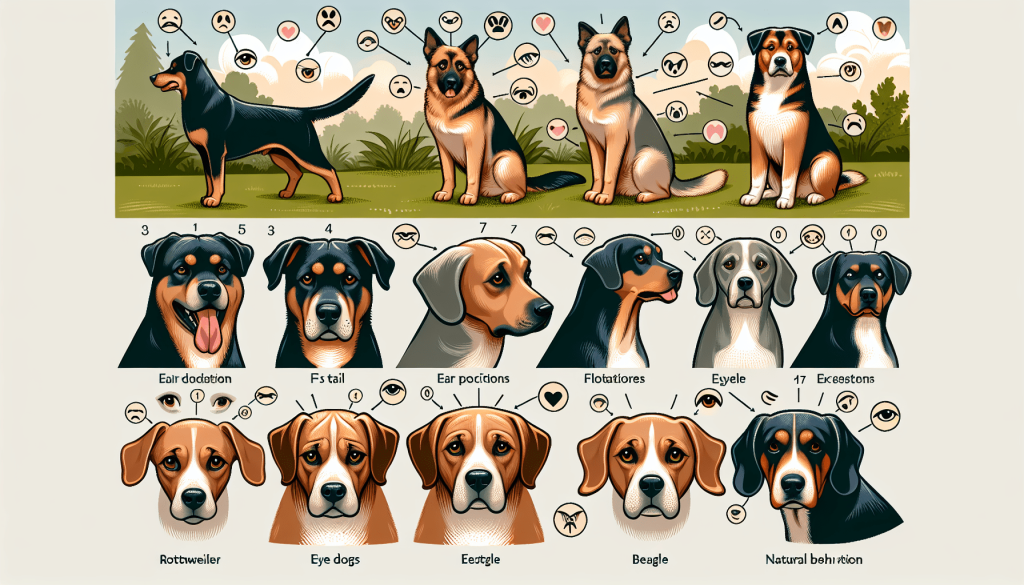
Congratulations on taking the first step towards understanding your furry companion! In this beginner’s guide to understanding dog body language, we will unravel the mysterious ways in which our four-legged friends communicate with us. From wagging tails to confident stances, you’ll uncover the hidden messages behind their movements and expressions. So, get ready to embark on an exciting journey of decoding your dog’s behavior, strengthening your bond, and becoming a true dog whisperer!
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Importance of Understanding Dog Body Language
Why is it important to understand dog body language?
Understanding dog body language is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it allows us to effectively communicate with our furry friends. Dogs use their body language as a means of expressing their emotions, needs, and intentions. By being able to interpret their signals, we can better understand what they are trying to communicate to us, ultimately deepening our bond and strengthening our relationship.
Secondly, understanding dog body language can help prevent misunderstandings and potential conflicts. Dogs have their unique ways of expressing fear, anxiety, and aggression. By being aware of these signs, we can identify when a dog is feeling uncomfortable or threatened, allowing us to adjust our behavior or remove our dog from potentially stressful situations.
Lastly, interpreting dog body language is essential for our own safety. By understanding their signals, we can recognize warning signs of aggression and take appropriate measures to prevent bites or other negative interactions. Overall, knowledge of dog body language enhances our ability to be responsible and caring dog owners.
How does understanding dog body language improve your relationship with your dog?
Understanding dog body language positively impacts our relationship with our dogs in numerous ways. Firstly, it allows us to build trust with our dogs. When we are able to accurately interpret their signals and respond appropriately, dogs feel understood, and their trust in us grows. This trust is the foundation for a strong and harmonious bond between a dog and their owner.
Secondly, understanding dog body language helps us meet our dogs’ needs and ensure their well-being. Dogs communicate their desires and discomfort through their body language, such as indicating when they want to play, when they are hungry, or when they are feeling unwell. By interpreting these signals, we can cater to their specific needs, ensuring they feel loved, cared for, and content.
Furthermore, interpreting dog body language allows us to provide appropriate socialization experiences for our dogs. We can recognize when our dogs are comfortable or uncomfortable in certain situations or with certain individuals, allowing us to make informed decisions about their social interactions. This leads to positive experiences and helps our dogs develop into well-adjusted and confident individuals.
Overall, understanding dog body language strengthens our bond with our dogs, ensures their safety and well-being, and fosters a positive and harmonious relationship.
Basic Dog Body Language Signals
Tail wagging
Tail wagging is one of the most well-known dog body language signals, but it is essential to understand that not all tail wagging indicates happiness or friendliness. The position of the tail, the speed, and the intensity of the wag can convey different messages.
A loose, relaxed wag with the tail held in a mid-position generally indicates a friendly and content dog. On the other hand, a tucked tail or a tail held high and stiff can suggest fear or aggression, respectively. It is also crucial to consider the rest of the dog’s body language when interpreting tail wagging, as tail position alone may not be sufficient to understand their emotions.
Ears
The position and movement of a dog’s ears can provide valuable insights into their mood and intentions. When a dog’s ears are relaxed and in a natural position, it typically indicates that they are calm and content. However, upright or forward-pointing ears can suggest attentiveness or excitement.
Conversely, flattened or pinned-back ears are often signs of fear, anxiety, or aggression. It is important to note that some dog breeds naturally have ears that are always in an upright position, so it’s crucial to consider the individual dog’s baseline ear position before making assumptions.
Eye contact
Eye contact is a significant component of dog communication. Direct eye contact can be seen as a challenge or threat, especially in dog-to-dog interactions. Avoid prolonged direct eye contact with unfamiliar dogs, as it may provoke aggressive responses.
However, with your own dog, gentle and soft eye contact can help establish a bond of trust. Dogs often use eye contact to seek reassurance or to convey their needs to their owners. Being able to understand and respond to their eye contact signals can strengthen the emotional connection between you and your furry companion.
Mouth and facial expressions
A dog’s mouth and facial expressions can reveal a wealth of information about their emotions and intentions. Relaxed, slightly open mouths with a lolling tongue generally indicate a calm and content dog.
However, tightly closed mouths, bared teeth, or a curled lip can indicate fear, aggression, or discomfort. Yawning can also be a sign of stress or anxiety in dogs. By paying attention to the nuances of their mouth and facial expressions, we can better understand our dogs’ emotional states and offer them appropriate support if needed.
Body Postures and Movements
The meaning behind different body postures
A dog’s body posture can communicate a variety of messages. Understanding these postures can help us gauge their level of confidence, fear, or aggression. Some common body postures include:
- Relaxed and loose body: This indicates a comfortable and friendly dog.
- Stiff and tense body: This may suggest fear, anxiety, or aggression.
- Crouched or lowered body: A dog in this position is often signaling submission or a lack of confidence.
- Raised hackles: Raised hair along the back can indicate arousal, excitement, or fear.
It is important to remember that body postures should always be considered in conjunction with other behavioral cues to accurately interpret a dog’s emotional state.
Types of movements and what they indicate
Dogs communicate through various movements, which can further enhance our understanding of their intentions and emotions. Some common movements and their meanings include:
- Slow, relaxed wagging of the entire body: It reflects happiness and friendliness.
- Bouncy or exaggerated movements: Dogs exhibiting this behavior are often excited and eager to engage in play.
- Freezing or immobile stance: This can be a sign of fear or uncertainty.
By studying a dog’s movements in different contexts, we can gain valuable insights into their current emotional state and respond accordingly.
Common Dog Body Language Behaviors
Play signals and invitations
When dogs engage in play, they often rely on specific body language signals to communicate their desire to play, establish boundaries, and avoid misunderstandings. Some common play signals include:
- Play bow: A dog will lower their front end while keeping their rear end elevated. This signals an invitation to play.
- Quick and darting movements: Dogs use rapid movements to invite chasing or playfully nip at each other.
Recognizing these play signals allows us to create safe and enjoyable play experiences for our dogs and prevent potential conflicts.
Submissive and dominant behaviors
In a social hierarchy, dogs naturally display submissive or dominant behaviors to establish and maintain their positions. Submissive behaviors include:
- Rolling onto their back, exposing their belly
- Tucking their tail between their legs
- Avoiding eye contact
Dominant behaviors, on the other hand, may include:
- Standing tall with a stiff posture
- Standing over or leaning on another dog
- Intense and prolonged eye contact
Understanding these behaviors can help us navigate social interactions and ensure harmony among dogs in multi-dog households or social settings.
Fear and anxiety signals
When dogs feel fearful or anxious, they exhibit specific body language signals to communicate their discomfort. These signals may include:
- Cowering or attempting to make themselves appear small
- Trembling or shaking
- Attempting to hide or retreat
Recognizing these signs of fear and anxiety allows us to provide our dogs with a safe and supportive environment, helping to alleviate their stress and build their confidence.
Aggression and warning signs
It is essential to recognize the warning signs of aggression in dogs to prevent potential injuries or conflicts. Some common aggressive body language signals include:
- Stiff, tense body posture
- Direct staring or staring with a hard, fixed gaze
- Growling or showing teeth
By identifying these warning signs, we can take appropriate action to defuse a potentially dangerous situation and keep ourselves and others safe.
Dog Body Language in Different Contexts
Body language during greetings
When dogs meet, their body language during greetings can provide valuable insights into their level of comfort and interest. Some common body language cues during greetings include:
- Tail wagging with a relaxed body: Indicates a friendly and open demeanor.
- Tail held high and stiff: Can suggest tension or potential aggression.
- A head turned to the side or avoiding direct eye contact: Indicates submissiveness or lack of interest.
Being mindful of these cues can help ensure positive and successful interactions between dogs.
Body language during play
During play, dogs exhibit specific body language cues to engage and communicate their intentions. Some common play body language signals include:
- Play bows: A dog will lower their front end while keeping their rear end elevated, inviting their playmate to engage.
- Soft facial expressions and relaxed mouths: Indicate a playful and friendly attitude.
- Gentle mouth mouthing or biting without aggression: Part of normal play behavior.
Understanding these signals allows us to monitor play sessions and ensure that all dogs involved are having fun and playing in a safe manner.
Body language during feeding
A dog’s behavior during feeding time can tell us a lot about their relationship with food and any potential resource guarding tendencies. Signs of discomfort around food may include:
- Growling or snapping when approached while eating
- Stiffening or freezing when someone gets too close to their food bowl
- Gulping or eating quickly, indicating anxiety or uncertain food availability
By respecting their need for space during meal times and addressing any food-related issues promptly, we can ensure a stress-free feeding routine for our dogs.
Body language during training
During training sessions, a dog’s body language can provide insights into their level of engagement, understanding, and comfort. Some positive indicators include:
- Wagging tails or relaxed posture: Suggest a willingness to participate and eagerness to learn.
- Focused attention on the handler: Indicates responsiveness to commands and cues.
Conversely, signs of stress or discomfort can include tense body postures, avoidance behaviors, or excessive panting. Recognizing these signals helps us modify our training approaches to ensure a positive and enjoyable learning experience for our dogs.
Understanding Tail Wagging and Other Tail Signals
Different types of tail wagging and their meanings
Tail wagging is a form of communication that can convey a range of emotions and intentions. Some different types of tail wagging and their possible meanings include:
- Fast, wide wag: Indicates excitement and happiness.
- Slow wag with a low tail: May suggest caution or uncertainty.
- Stiffly held tail wag: Can indicate tension or potential aggression.
It is essential to consider the context and the rest of the dog’s body language when interpreting tail wagging.
Other tail signals to look out for
In addition to wagging, a dog’s tail can provide additional signals about their emotional state. Some other tail signals to look out for include:
- Tucked tail: Suggests fear or submission.
- Raised tail held high and stiff: Can indicate alertness or potential aggression.
- Wagging tail held low or between the legs: May suggest anxiety or fear.
By paying attention to these subtle cues, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of our dogs’ emotions and respond accordingly.
Interpreting Ear Positions and Expressions
Meanings behind different ear positions
A dog’s ear positions can reveal valuable insights into their mood and intentions. Some common ear positions and their meanings include:
- Erect and forward-pointing ears: Indicate attentiveness, curiosity, or excitement.
- Relaxed, floppy ears: Suggest a calm and content dog.
- Pinned back or flattened ears: May signal fear, anxiety, or submission.
It is crucial to consider the individual dog’s natural ear shape and position to accurately interpret their emotions based on their ear positions.
Ear expressions and their significance
In addition to ear positions, a dog’s ear expressions can provide further information about their emotional state. Some common ear expressions and their significance include:
- Perked ears: Suggest interest and attentiveness.
- One ear slightly back: Can indicate hesitation or uncertainty.
- Ears tightly plastered to the head: May suggest fear or distress.
By observing these subtle ear movements and expressions, we can gain deeper insights into our dogs’ emotions and respond accordingly.
Reading Eye Contact and Blinking
Importance of eye contact in dog communication
Eye contact plays a significant role in dog communication, but its meaning can vary depending on the context and the individuals involved. For dogs, direct eye contact can be a sign of challenge or threat, especially in dog-to-dog interactions. Avoid prolonged, intense eye contact with unfamiliar dogs to prevent potential conflicts.
However, with your own dog, gentle and relaxed eye contact can help establish a bond of trust. Dogs often use eye contact to seek reassurance or to convey their needs to their owners. By understanding and responding to their eye contact signals, we can deepen our connection with our furry companions.
Different eye contact signals
While direct eye contact can be perceived as threatening in certain situations, dogs also use eye contact to communicate various messages. Some different eye contact signals and their possible meanings include:
- Soft, relaxed eye contact: Suggests trust, comfort, and positive engagement.
- Hard stare or prolonged direct eye contact: Should be avoided, as it can be seen as confrontational or challenging.
- Avoidance of eye contact or looking away: Can indicate submissiveness or fear.
Interpreting these eye contact signals allows us to better understand our dogs’ emotions and provides valuable information for successful interactions.
Interpreting blinking and eye movements
In addition to eye contact, blinking and other eye movements can also reveal important information about a dog’s emotional state. Some common eye movements and their possible meanings include:
- Slow blinking: Can indicate relaxation, trust, and contentment.
- Rapid or exaggerated blinking: May suggest discomfort, stress, or anxiety.
- Dilated pupils: Can indicate excitement, fear, or heightened arousal.
By paying attention to these eye movements, we can gain a deeper understanding of our dogs’ emotional well-being and respond appropriately to their needs.
Decoding Mouth and Facial Expressions
Understanding different mouth movements and gestures
A dog’s mouth movements and gestures can communicate various messages about their emotions and intentions. Some different mouth movements and their significance include:
- Relaxed, slightly open mouth with a lolling tongue: Indicates a calm and content dog.
- Tightly closed mouth with bared teeth: Can signify fear, agitation, or aggression.
- Panting excessively or with rapid, shallow breaths: May indicate stress or discomfort.
By observing and understanding these mouth movements, we can gain insights into our dogs’ current emotional state and respond accordingly.
Significance of facial expressions in dog body language
A dog’s facial expressions can provide valuable clues about their feelings and intentions. Some common facial expressions and their meanings include:
- Relaxed facial muscles, soft eyes, and open mouth: Indicate a calm and content dog.
- Wrinkled forehead or raised upper lip: May signal anxiety, fear, or aggression.
- Yawning or lip licking: Can be signs of stress or discomfort.
By paying attention to these facial expressions, we can better understand our dogs and provide the support they need in different situations.
Tips for Interpreting Dog Body Language
Observe the overall body language
When interpreting dog body language, it is essential to consider the overall context and the dog’s entire body language rather than focusing on a single cue. Different body language signals often work in conjunction with each other, and understanding the entire picture helps ensure accurate interpretation.
Consider the context and environment
Context plays a crucial role in understanding dog body language. What may be a friendly gesture in one context could be a sign of anxiety or aggression in another. Consider the environment, the presence of other dogs or people, and the dog’s previous experiences to appropriately interpret their body language signals.
Pay attention to the dog’s individual personality
Every dog is unique and may have their own individual quirks. Understanding your dog’s baseline body language is essential for accurate interpretation. Pay attention to their typical behaviors and expressions to better understand their emotional states and responses to different situations.
Seek professional advice if unsure
If you are unsure about a dog’s body language or if you have concerns about your dog’s behavior, it is always prudent to seek the advice of a qualified professional, such as a veterinarian or a certified dog behaviorist. They can provide guidance, support, and specific recommendations tailored to your dog’s individual needs.
By following these tips and continuously expanding your knowledge of dog body language, you can enhance your relationship with your furry friend and ensure their well-being and happiness. Understanding and responding to their nonverbal cues allows you to communicate effectively, build trust, and create a loving and harmonious bond with your canine companion.